Private cloud computing is model of cloud computing.. that involves distinct & secure cloud based environment in which only specific organization can operate. As opposed to public clouds where resources are shared among multiple tenants private clouds are dedicated to single organization offering enhanced control security & customization options.
The concept of private cloud emerged as response to security & compliance concerns associated with public cloud services. It combines many of benefits of cloud computing such as scalability flexibility & efficiency with security & control of on premises infrastructure.
READ MORE : How To Connect Nova Lite To Dongle
Key Characteristics of Private Cloud
Private clouds share several characteristics with other cloud models but have some distinct features:
1. Dedicated Resources: All hardware & software resources are devoted to & accessible by one organization.
2. Enhanced Security & Control: organization has greater control over its environment & can implement stricter security measures.
3. Customization: Private clouds can be tailored to meet specific organizational requirements & integrate with existing systems.
4. Scalability: Resources can be scaled up or down based on demand similar to public clouds.
5. Self Service: Users can provision & manage resources through self service portals.
6. Measured Service: Resource usage is monitored controlled & reported providing transparency for both provider & consumer of utilized services.
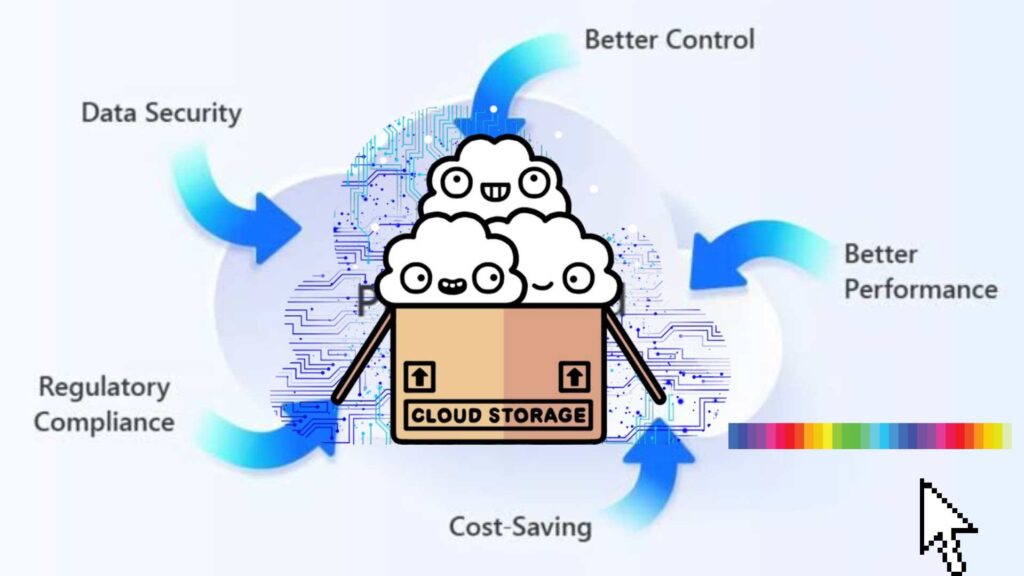
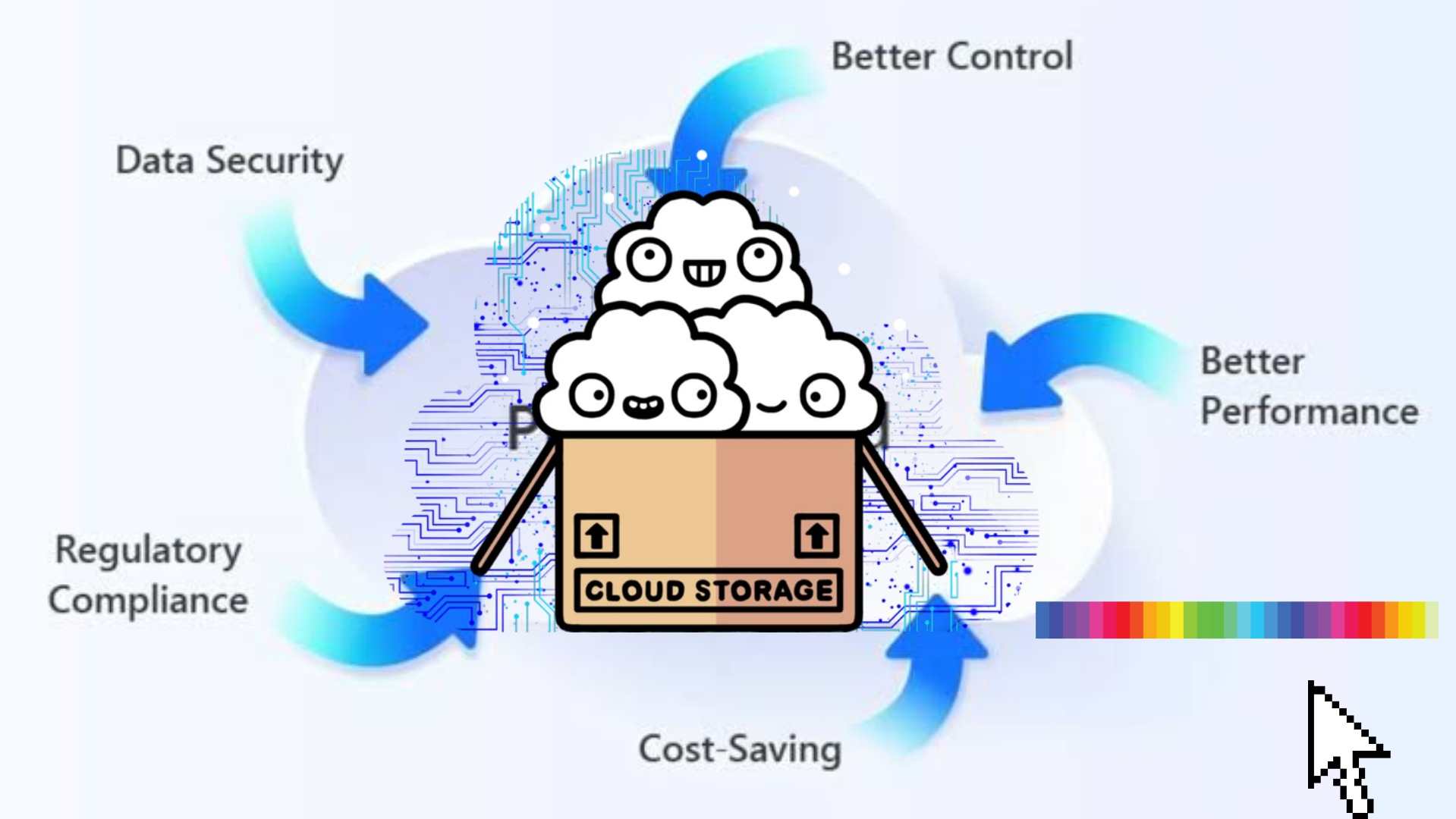
Benefits of Private Cloud
Private cloud computing offers several advantages to organizations:
1. Improved Security & Compliance: With greater control over infrastructure organizations can implement robust security measures & ensure compliance with industry regulations.
2. Enhanced Performance: Dedicated resources often result in better performance compared to shared public cloud environments.
3. Customization & Flexibility: Organizations can tailor cloud environment to their specific needs & easily integrate with existing IT infrastructure.
4. Cost Predictability: While initial investments may be higher private clouds can offer more predictable ongoing costs compared to public cloud services.
5. Data Sovereignty: Organizations can ensure.. that their data remains within specific geographic boundaries which is crucial for compliance with data protection regulations.
6. Resource Optimization: Private clouds allow for better utilization of existing hardware & software resources.
7. Improved Reliability: With direct control over infrastructure organizations can implement robust disaster recovery & business continuity measures.
Challenges & Considerations
While private clouds offer numerous benefits they also come with certain challenges:
1. Initial Costs: Setting up private cloud requires significant upfront investment in hardware software & expertise.
2. Complexity: Designing implementing & managing private cloud can be complex & may require specialized skills.
3. Scalability Limitations: While scalable private clouds may have upper limits based on organizations infrastructure capacity.
4. Ongoing Maintenance: Organizations are responsible for maintaining & updating entire cloud stack which can be resource intensive.
5. Potential for Underutilization: If not properly managed private clouds can lead to underutilized resources reducing cost effectiveness.
6. Vendor Lock in: Depending on technologies chosen organizations may face challenges in migrating to different platforms in future.
Private Cloud vs Public Cloud vs Hybrid Cloud
Understanding differences between private public & hybrid clouds is crucial for organizations considering cloud adoption:
Private Cloud:
● Dedicated to single organization
● Greater control & security
● Higher upfront costs
● Suitable for organizations with strict security & compliance requirements
Public Cloud:
● Shared infrastructure among multiple tenants
● Lower upfront costs & pay as you go model
● Less control over underlying infrastructure
● Suitable for organizations with fluctuating workloads & less sensitive data
Hybrid Cloud:
● Combination of private & public cloud services
● Offers flexibility to run workloads in most appropriate environment
● Allows for data & application portability
● Suitable for organizations looking to balance control & cost effectiveness
Private Cloud Architecture & Components
A typical private cloud architecture consists of several key components:
1. Compute Layer: This includes physical or virtual servers.. that provide processing power for applications & services.
2. Storage Layer: Provides data storage capabilities often using technologies like Storage Area Networks (SAN) or Network Attached Storage (NAS).
3. Network Layer: Ensures connectivity between different components of cloud & to external networks.
4. Virtualization Layer: Enables creation & management of virtual machines & containers.
5. Management Layer: Provides tools for monitoring orchestration & automation of cloud resources.
6. Security Layer: Implements various security measures including firewalls encryption & access controls.
7. Self Service Portal: Allows users to request & manage resources without IT intervention.
8. Service Catalog: Defines services available to users within private cloud.
Implementation Strategies
Organizations can implement private clouds through various strategies:
1. On Premises Private Cloud: cloud infrastructure is hosted within organizations own data center. This offers maximum control but requires significant expertise & resources.
2. Hosted Private Cloud: cloud is hosted by third party provider but on dedicated hardware. This reduces need for in house expertise while still providing many private cloud benefits.
3. Managed Private Cloud: Similar to hosted private cloud but provider also manages cloud infrastructure. This further reduces burden on organizations IT team.
4. Software Defined Data Center (SDDC): This approach uses software to control & manage all data center resources providing greater flexibility & efficiency.
5. Converged & Hyperconverged Infrastructure: These pre integrated solutions combine compute storage & networking into single system simplifying private cloud deployment.
Security & Compliance in Private Cloud
Security is often primary driver for adopting private clouds. Key security considerations include:
1. Access Control: Implementing robust authentication & authorization mechanisms.
2. Data Encryption: Ensuring data is encrypted both at rest & in transit.
3. Network Security: Using firewalls intrusion detection/prevention systems & network segmentation.
4. Compliance Management: Ensuring cloud environment meets relevant regulatory requirements (e.g. GDPR HIPAA).
5. Security Monitoring: Implementing continuous monitoring & logging to detect & respond to security incidents.
6. Data Loss Prevention: Implementing measures to prevent unauthorized data exfiltration.
7. Disaster Recovery & Business Continuity: Ensuring data & applications can be recovered in case of disaster.
Management & Monitoring
Effective management & monitoring are crucial for private cloud success:
1. Cloud Management Platforms: Tools like VMware vRealize OpenStack or Microsoft System Center provide comprehensive management capabilities.
2. Automation & Orchestration: Using tools to automate routine tasks & orchestrate complex workflows.
3. Performance Monitoring: Implementing systems to monitor resource usage application performance & user experience.
4. Capacity Planning: Regularly assessing resource utilization & planning for future needs.
5. Cost Management: Implementing chargeback or showback mechanisms to track & optimize cloud costs.
6. Service Level Agreement (SLA) Management: Defining & monitoring SLAs for different services within private cloud.
Use Cases & Industry Applications
Private clouds are particularly well suited for certain use cases & industries:
1. Financial Services: Banks & insurance companies often use private clouds to maintain control over sensitive financial data while leveraging cloud benefits.
2. Healthcare: Private clouds help healthcare providers comply with regulations like HIPAA while improving IT efficiency.
3. Government: Many government agencies opt for private clouds to maintain data sovereignty & meet stringent security requirements.
4. Large Enterprises: Organizations with substantial existing IT investments often find private clouds an effective way to modernize their infrastructure.
5. Research & Development: Private clouds can provide computing power needed for complex simulations & data analysis while keeping intellectual property secure.
6. Telecommunications: Telecom companies use private clouds to manage network functions & customer data securely.
7. Education: Universities & research institutions leverage private clouds for high performance computing & to secure student data.
Future Trends in Private Cloud Computing
Several trends are shaping future of private cloud computing:
1. Edge Computing Integration: Private clouds are extending to edge to support IoT & low latency applications.
2. AI & Machine Learning: Private clouds are increasingly being used to host AI & ML workloads leveraging specialized hardware like GPUs.
3. Containerization & Microservices: adoption of container technologies like Kubernetes is making private clouds more agile & efficient.
4. Multi Cloud & Hybrid Strategies: Organizations are increasingly using private clouds as part of broader multi cloud or hybrid cloud strategies.
5. Automation & Self Healing: Advanced automation capabilities including self healing systems are reducing management burden of private clouds.
6. Green Computing: Energy efficient technologies & practices are being incorporated into private cloud designs to reduce environmental impact.
7. Quantum Computing: As quantum computing evolves private clouds may play role in securely hosting & managing quantum resources.
Private cloud computing represents powerful approach for organizations seeking to leverage benefits of cloud computing while maintaining control over their IT environment. By offering enhanced security customization & performance private clouds address many of concerns associated with public cloud adoption.
implementing & managing private cloud requires careful planning significant investment & ongoing commitment. Organizations must carefully assess their needs resources & long term IT strategy when considering private cloud approach.
As cloud technologies continue to evolve private clouds are likely to remain an important part of IT landscape particularly for organizations dealing with sensitive data or complex regulatory requirements. integration of emerging technologies like edge computing AI & advanced automation will further enhance capabilities of private clouds making them an increasingly attractive option for wide range of organizations.
Ultimately success of private cloud initiative depends on aligning cloud strategy with business objectives ensuring proper governance & management & continuously optimizing environment to meet changing organizational needs. With right approach private clouds can provide powerful foundation for digital transformation enabling organizations to innovate faster operate more efficiently & respond more effectively to market changes.