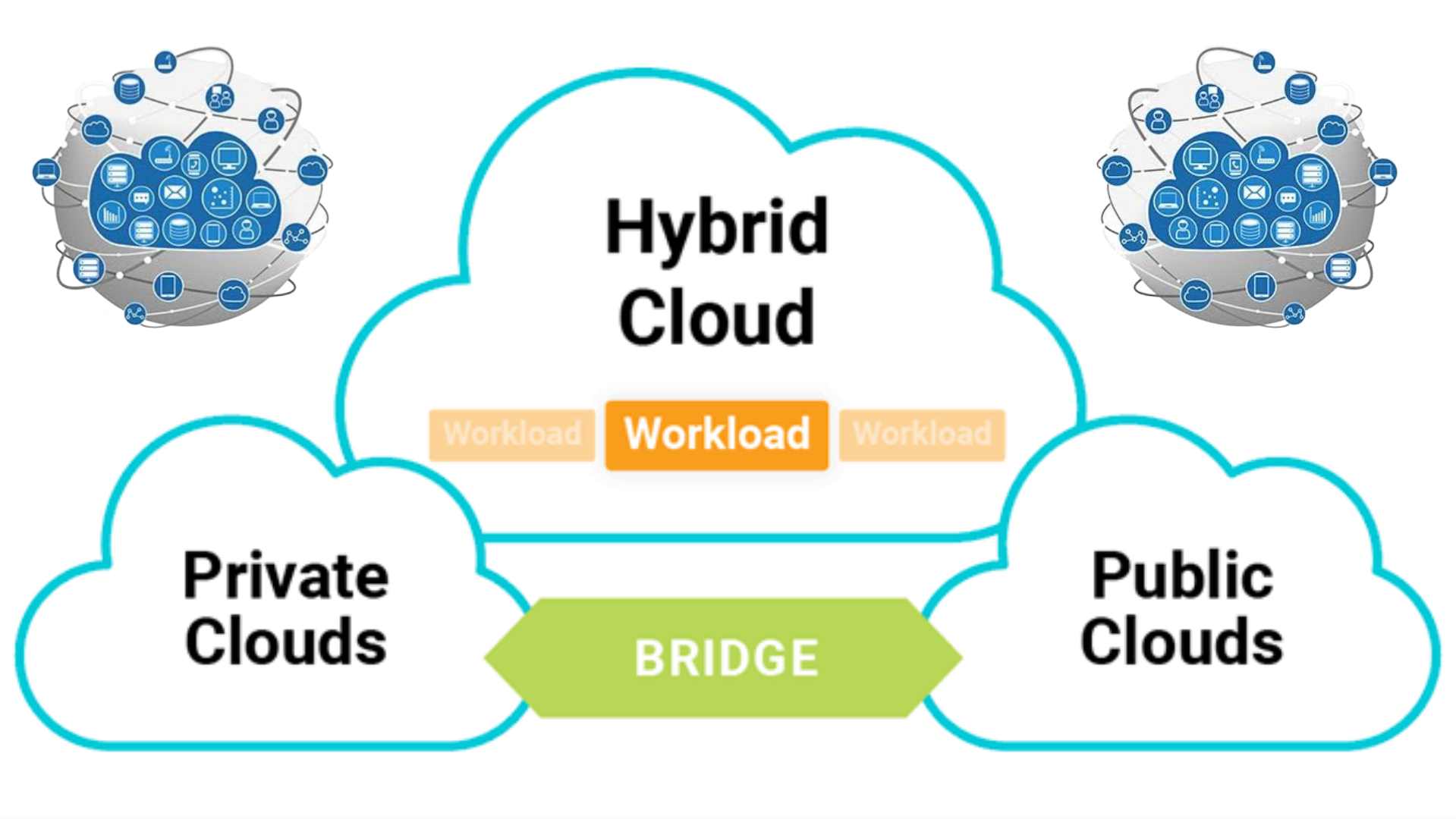
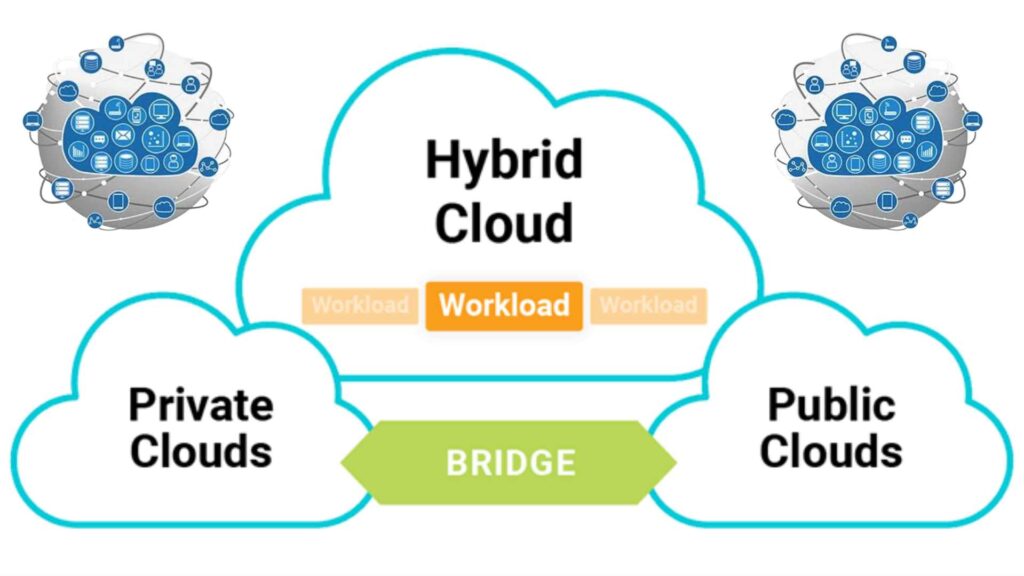
Hybrid cloud has emerged as powerful & flexible approach to cloud computing combining best of both private & public cloud environments. This model allows organizations to leverage scalability & cost effectiveness of public cloud services while maintaining control over sensitive data & critical applications in private cloud or on premises infrastructure.
The concept of hybrid cloud has gained significant traction in recent years as businesses seek to optimize their IT infrastructure improve agility & drive digital transformation. By adopting hybrid cloud strategy organizations can create more dynamic & adaptable IT environment.. that can respond quickly to changing business needs & market conditions.
READ MORE: Private Cloud Computing: Comprehensive Guide 2024
At its core hybrid cloud is about creating seamless integration between different cloud environments & traditional IT infrastructure. This integration enables workloads to move freely between environments data to be shared securely & applications to leverage most appropriate resources based on performance cost & security requirements.
As we delve deeper into world of hybrid cloud well explore its key components benefits challenges & implementation strategies providing comprehensive understanding of this transformative technology.
Key Components of Hybrid Cloud
A hybrid cloud environment typically consists of following key components:
- Private Cloud: This is cloud computing environment dedicated to single organization. It can be hosted on premises or by third party provider. Private clouds offer greater control over data security & compliance.
- Public Cloud: These are cloud services provided by third party vendors such as Amazon Web Services (AWS) Microsoft Azure or Google Cloud Platform (GCP). Public clouds offer scalability cost effectiveness & wide range of services.
- On premises Infrastructure: This includes traditional data center resources such as servers storage & networking equipment.. that are owned & operated by organization.
- Cloud Management Platform: software layer.. that provides unified interface for managing & orchestrating resources across different cloud environments.
- Network Connectivity: Robust & secure network connections between different cloud environments & on premises infrastructure are crucial for hybrid cloud operations.
- Data Integration & Management: Tools & processes for synchronizing & managing data across multiple environments.
- Identity & Access Management (IAM): Systems for managing user identities access controls & authentication across hybrid cloud environments.
- Security & Compliance Tools: Solutions for ensuring data protection threat detection & regulatory compliance across all components of hybrid cloud.
Understanding these components & how they interact is essential for designing & implementing an effective hybrid cloud strategy.
Benefits of Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid cloud offers numerous benefits to organizations making it an attractive option for businesses of all sizes. Some of key advantages include:
- Flexibility & Scalability: Hybrid cloud allows organizations to scale resources up or down based on demand leveraging public cloud for burst capacity during peak periods while maintaining core operations on private infrastructure.
- Cost Optimization: By utilizing public cloud resources for non sensitive workloads & maintaining critical applications on premises or in private cloud organizations can optimize their IT spending & achieve balance between capital & operational expenses.
- Improved Security & Compliance: Hybrid cloud enables organizations to keep sensitive data & applications in private environment while leveraging public cloud services for less critical workloads helping to meet regulatory requirements & enhance overall security posture.
- Business Continuity & Disaster Recovery: Hybrid cloud architectures can enhance resilience by providing multiple environments for data backup & recovery ensuring business continuity in event of disaster.
- Accelerated Innovation: Access to cutting edge cloud services & technologies allows organizations to rapidly prototype & deploy new applications fostering innovation & agility.
- Workload Optimization: Hybrid cloud enables organizations to place workloads in most appropriate environment based on performance cost & security requirements.
- Legacy System Integration: Hybrid cloud provides bridge between legacy systems & modern cloud based applications allowing organizations to modernize their IT infrastructure gradually.
- Data Sovereignty & Localization: For organizations operating in multiple regions hybrid cloud allows for compliance with data residency requirements by keeping certain data within specific geographical boundaries.
- Vendor Lock in Avoidance: By distributing workloads across multiple environments organizations can reduce dependence on single cloud provider & maintain greater flexibility in their IT strategy.
- Improved Performance: Hybrid cloud architectures can enhance application performance by placing workloads closer to end users or leveraging specialized cloud services for compute intensive tasks.
These benefits make hybrid cloud an attractive option for organizations looking to modernize their IT infrastructure while maintaining control over critical assets & data.
Challenges in Hybrid Cloud Implementation
While hybrid cloud offers numerous benefits it also presents several challenges.. that organizations must address for successful implementation:
- Complexity: Managing multiple cloud environments & on premises infrastructure can be complex requiring specialized skills & tools to ensure seamless integration & operation.
- Data Management & Consistency: Maintaining data consistency & synchronization across different environments can be challenging especially for applications.. that require real time data access.
- Security & Compliance: Ensuring consistent security policies & maintaining regulatory compliance across diverse environments can be complex & resource intensive.
- Network Performance & Latency: Hybrid cloud architectures may introduce network latency & bandwidth constraints potentially impacting application performance.
- Cost Management: While hybrid cloud can optimize costs it can also lead to unexpected expenses if not managed properly. Organizations need robust cost monitoring & optimization strategies.
- Skill Gap: Implementing & managing hybrid cloud environments requires diverse skill set.. that may not be readily available within many organizations.
- Vendor Management: Working with multiple cloud providers & vendors can be challenging requiring careful contract negotiation & relationship management.
- Application Compatibility: Not all applications are designed to work seamlessly across different cloud environments potentially requiring refactoring or re architecting.
- Data Migration: Moving large volumes of data between different environments can be time consuming & complex potentially causing disruptions to business operations.
- Governance & Control: Maintaining visibility & control over resources spread across multiple environments can be challenging requiring robust governance frameworks & tools.
- Service Level Agreements (SLAs): Managing & meeting SLAs across diverse environments can be complex especially when dealing with multiple providers.
- Cultural Resistance: Adopting hybrid cloud strategy often requires significant changes to IT processes & organizational culture which may face resistance from some stakeholders.
Addressing these challenges requires careful planning investment in appropriate tools & technologies & ongoing management & optimization of hybrid cloud environment.
Hybrid Cloud Architecture
Well designed hybrid cloud architecture is crucial for realizing benefits of this approach while mitigating its challenges. Key components & considerations in hybrid cloud architecture include:
Multi cloud Strategy: Many hybrid cloud architectures incorporate services from multiple public cloud providers alongside private cloud resources. This approach can optimize performance cost & functionality.. but requires careful management.
Network Architecture: robust & secure network is backbone of any hybrid cloud environment. This typically includes:
- High speed low latency connections between on premises & cloud environments
- Software defined networking (SDN) for flexible network management
- Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) or dedicated connections for secure data transfer
Data Management Layer: This component handles data synchronization replication & migration between different environments. It may include:
- Data lakes or data warehouses for centralized storage
- ETL (Extract Transform Load) tools for data integration
- Caching mechanisms for improved performance
Identity & Access Management (IAM): centralized IAM system is crucial for maintaining security across hybrid environments. This typically includes:
- Single Sign On (SSO) capabilities
- Multi factor authentication (MFA)
- Role based access control (RBAC)
Orchestration & Automation: Tools & platforms for managing & automating workloads across different environments such as:
- Kubernetes for container orchestration
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC) tools like Terraform or CloudFormation
- Cloud management platforms for unified resource management
Security Architecture: comprehensive security strategy.. that encompasses all components of hybrid cloud including:
- Encryption for data at rest & in transit
- Network segmentation & microsegmentation
- Intrusion detection & prevention systems (IDS/IPS)
- Security information & event management (SIEM) systems
Monitoring & Analytics: Tools for monitoring performance usage & health across all environments:
- Centralized logging & monitoring solutions
- Application performance monitoring (APM) tools
- AI powered analytics for predictive maintenance & optimization
Disaster Recovery & Business Continuity: Strategies & tools for ensuring resilience & data protection:
- Multi site replication
- Automated failover mechanisms
- Regular backup & recovery testing
API Management: robust API strategy is crucial for enabling integration between different components of hybrid cloud:
- API gateways for managing & securing API traffic
- API development & lifecycle management tools
Edge Computing Integration: For organizations leveraging edge computing hybrid cloud architecture should include provisions for integrating edge devices & processing:
- Edge gateways for data aggregation & preprocessing
- Local compute & storage resources at edge locations
When designing hybrid cloud architecture its important to consider specific needs & constraints of organization including regulatory requirements existing infrastructure & long term business goals. architecture should be flexible enough to evolve as technology & business needs change over time.
Implementing Hybrid Cloud
Implementing hybrid cloud strategy requires careful planning & execution. Heres general approach to hybrid cloud implementation:
Assessment & Planning:
- Evaluate current IT infrastructure & applications
- Identify business goals & requirements
- Develop comprehensive cloud strategy aligned with business objectives
- Assess security & compliance requirements
Workload Analysis & Categorization:
- Analyze existing workloads & data
- Categorize workloads based on factors such as sensitivity performance requirements & regulatory constraints
- Determine which workloads are suitable for public cloud private cloud or on premises environments
Choose Cloud Providers & Tools:
- Select public cloud providers based on requirements & compatibility
- Choose private cloud platform or on premises infrastructure solution
- Identify necessary tools for integration management & monitoring
Design Hybrid Cloud Architecture:
- Develop detailed architecture plan including network design security measures & data management strategies
- Plan for scalability & future growth
- Design for high availability & disaster recovery
Develop Migration Strategy:
- Prioritize workloads for migration
- Choose appropriate migration methods (e.g. lift and shift re platforming or re architecting)
- Develop phased migration plan to minimize disruption
Implement Core Infrastructure:
- Set up network connections between environments
- Implement identity & access management systems
- Deploy necessary management & monitoring tools
Migration & Integration:
- Begin migrating workloads according to migration plan
- Integrate on premises systems with cloud services
- Implement data synchronization & replication mechanisms
Security Implementation:
- Deploy security measures across all environments
- Implement encryption access controls & monitoring systems
- Conduct security testing & audits
Testing & Optimization:
- Conduct thorough testing of all migrated applications & services
- Optimize performance & resource allocation
- Refine security measures based on testing results
Training & Change Management:
- Provide training for IT staff on new tools & processes
- Develop & implement change management processes
- Educate end users on any changes to application access or usage
Ongoing Management & Optimization:
- Continuously monitor performance & costs
- Regularly review & update security measures
- Optimize resource allocation & workload placement
- Stay informed about new cloud services & technologies
Documentation & Governance:
- Develop comprehensive documentation of hybrid cloud environment
- Implement governance policies & procedures
- Establish regular review & audit processes
Implementing hybrid cloud is an ongoing process.. that requires continuous evaluation & optimization. As technology evolves & business needs change hybrid cloud strategy should be regularly reviewed & adjusted to ensure it continues to meet organizational objectives.